


Unless you have a top-secret time machine, there’s no way to guarantee the future price of a cryptocurrency — but that doesn’t mean traders can’t make educated guesses on their favorite coins. In fact, as traders study price graphs of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH), they may notice certain patterns arising.
Many of these chart patterns seem to precede significant movements in a cryptocurrency’s price, making them valuable signals for astute traders. Although crypto chart patterns aren’t always accurate, they’ve become a common way for market participants to determine key price levels when setting up trades.
Learning the basics of price chart patterns can put traders in a better position to assess their risk and set precise order types when entering the volatile crypto space. Price patterns don’t guarantee success, but they’re valuable indicators to add to a crypto trading toolkit.
What Are Crypto Chart Patterns?
Crypto chart patterns are recognizable forms or shapes on a cryptocurrency’s price graph that traders use to study market psychology and predict the likelihood of future movements. Searching for crypto chart patterns is a branch of technical analysis, which analyzes visual data on a coin’s price chart rather than fundamental metrics like a coin’s total supply or market capitalization. When traders search for candlestick chart patterns, they focus on well-documented images with historical precedence for indicating upward (bullish), downward (bearish), or sideways price action.
Benefits and Risks of Analyzing Candlestick Chart Patterns
Predicting prices with funny-sounding patterns like “Bart Simpson’s spiky hair” isn’t the most scientific way of studying the crypto market. Nevertheless, even seemingly silly chart formations could be useful.
Pros of Analyzing Crypto Chart Patterns
Defines price levels: Traders use crypto chart patterns to visualize attractive prices to open and close positions. Before buying or selling, traders know where to set their stop-losses and take-profit orders to remove erratic emotions from their trading decisions.
Provides a glimpse into price probabilities: Although price patterns don’t always turn out as expected, they give traders valuable information on market sentiment and whether a cryptocurrency has a bullish or bearish bias. When combined with other technical indicators and fundamental analysis, chart patterns help traders develop a thesis and determine the likely direction of an asset.
Easy to spot: Once traders grow familiar with the basic crypto patterns, it’s easier to see these formations at a glance. Some trading platforms also use software tools to help traders draw or discover chart patterns.
Cons of Analyzing Crypto Chart Patterns
Inconsistent results: No matter how often a chart pattern precedes a bullish or bearish price move, there are no guarantees these patterns follow an expected trajectory. Crypto patterns are probability indicators rather than set-in-stone laws, and it’s common for coins to move unexpectedly.
Room for interpretive error: Crypto chart patterns are often inconsistent because they're highly subjective. Each trader may see different patterns and arrive at different conclusions depending on their skill in reading crypto charts and the timeframes they’re researching.
Doesn’t account for fundamental analysis: Sometimes, fundamental events like a network upgrade or tweaks to a cryptocurrency’s tokenomics have major impacts on a crypto asset’s price. Traders who solely focus on technical patterns don’t account for the price implications of fundamental news, which may invalidate the patterns they’ve identified.
How to Identify Crypto Trading Patterns: A Few Tips
Think of searching for crypto chart patterns like studying clouds for weather predictions. Instead of looking for random and unique shapes in the sky, meteorologists know the traits associated with specific cloud varieties (e.g., nimbostratus or cumulus) and whether these clouds correlate with fair or foul weather. Similarly, crypto traders first study hallmark chart patterns — like bull flags, bear flags, and double tops — and what these shapes typically indicate.
After traders have a foundation in common chart patterns, they use their knowledge to scan current crypto price graphs and make calculated bets based on the images they see. For the greater odds of success, crypto traders focus on looking for well-established patterns rather than projecting new images onto price feeds. As traders interpret a cryptocurrency’s price patterns, they calculate their preferred “risk-return” profile — in other words, how much money traders are willing to lose to potentially profit off of a trade.
Although price chart patterns often have bullish or bearish biases, there are never guarantees they’ll turn out as expected. Just as weather forecasts aren’t always correct, chart patterns don’t accurately predict the future every time. Experienced crypto traders define their maximum loss potential ahead of a trade with orders such as “stop-losses” to get out of a losing position. By defining risk and reward ahead of time, crypto traders add predictability to their trades.
Crypto Patterns Cheat Sheet: Common Crypto Graph Patterns to Know
The more people stare at crypto price charts, the more patterns they seem to invent. Although there’s an endless list of possible images on crypto graphs, a few are common knowledge in crypto trading circles.
Bull or Bear Flags
Flag patterns start with a long green or red candlestick followed by a brief phase of sideways price action or a downtrend. The first part of this pattern is known as the “flagpole,” while the consolidation phase is the “flag,” and traders expect price action to follow the flagpole’s direction. Bull flags imply the price will rise, while bear flags suggest lower lows are incoming.

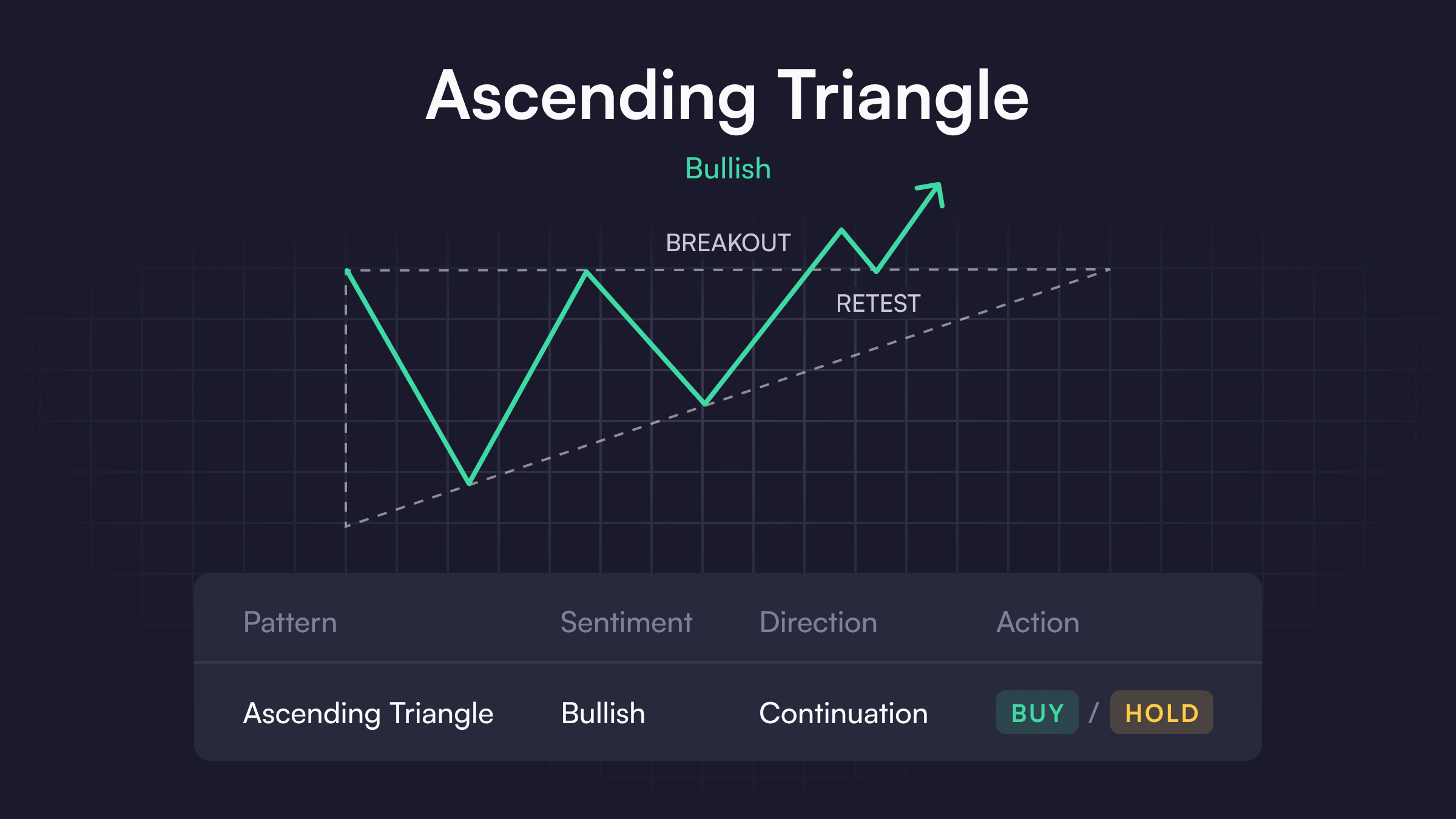
Ascending or Descending Triangles
In an ascending triangle, prices continuously post higher lows and bump against a vertical resistance level on the top of their price range until they create a third “point” in a triangle. The shape of a descending triangle is the same, except the price constantly hits a lower support line while narrowing with consistently lower highs. Although there’s no guarantee where prices go, the common thinking is that there is bias is up for ascending triangles and down for descending triangles.

Head and Shoulders
The “head and shoulders" pattern looks like two rounded shoulders with the highest price (or “head”) in the middle. Typically, these patterns signify a cryptocurrency is at a local top, and a selloff is imminent if prices break below the pattern’s “neckline.” However, when head and shoulders appear reversed, traders often view it as a sign of a price breakout.


Double Top
In a double-top formation, the price of a cryptocurrency rises to the same peak with an intermediate phase when it drops and bounces off of a support zone. Double tops are warning signs of a bearish reversal, especially if prices struggle to hold the previously defined support level after the second high.

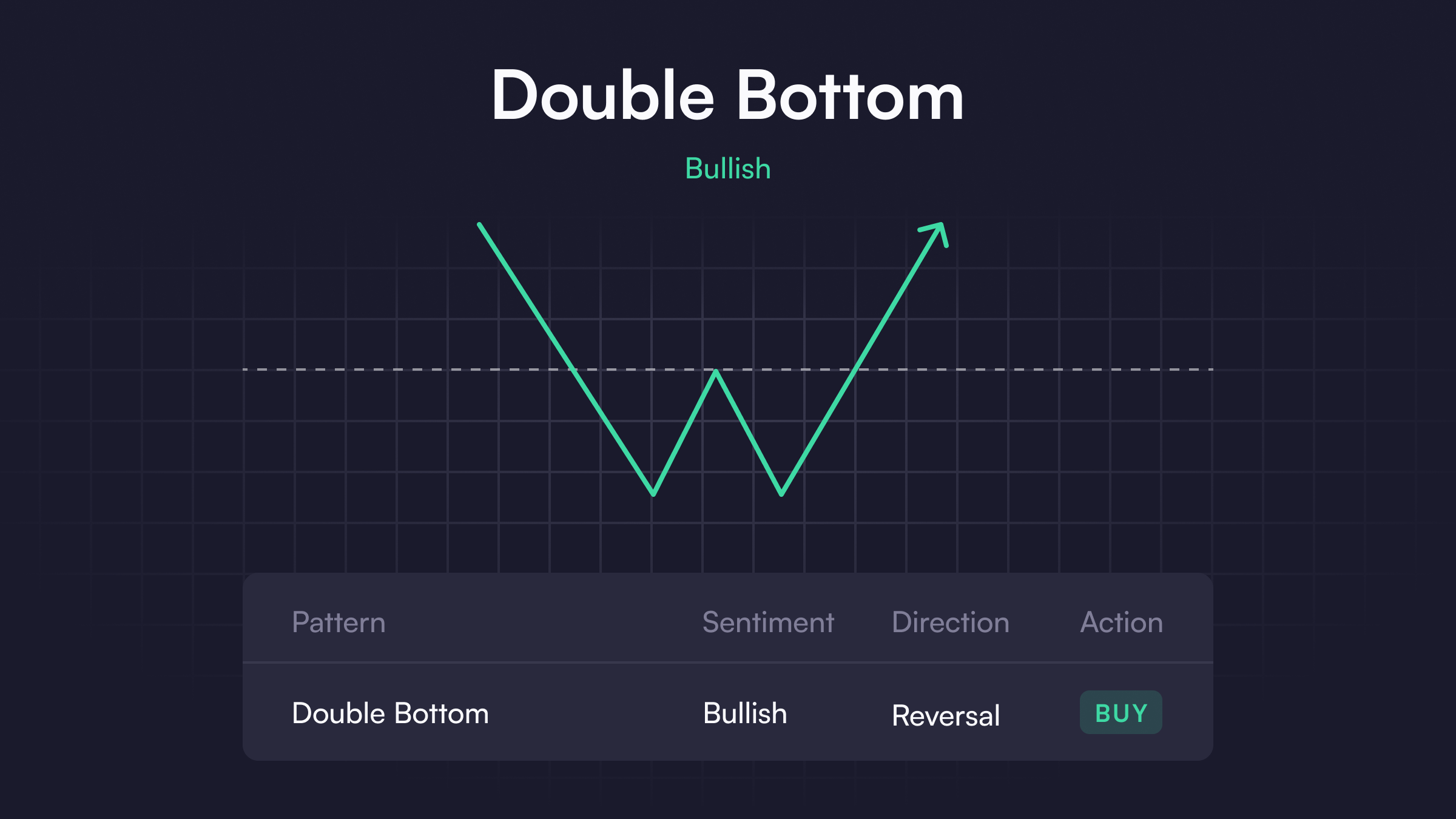
Double Bottom
Double bottoms are the inverse of double top patterns, often signaling a bullish trend reversal on the horizon. Instead of hitting two local highs and returning to a support band, double bottoms touch two price lows around the same level with a short rally in the middle. Traders typically expect a cryptocurrency to rally after bouncing off the second bottom.
Cup and Handle
The cup and handle candlestick pattern looks similar to a teacup and forms when a cryptocurrency is already in an uptrend. The “cup” portion takes shape after a token’s price hits a vertical resistance level and falls before rising again to the resistance zone. To get its distinctive “handle” portion, the cryptocurrency’s price needs to fall from resistance for about one-third the length of the cup before rising to resistance again. Traders often interpret this pattern as a “bullish continuation” and expect the cryptocurrency to continue rising after the handle appears.

Learn More Trading Tips on dYdX Academy
For more info on trading and using cryptocurrencies, check out the latest guides on dYdX Academy. From crypto wallet set-up and staking to derivatives and stop-losses, dYdX Academy has easy-to-understand articles to help everyone level up their crypto knowledge. Also, dYdX offers eligible traders a decentralized derivatives exchange for traders interested in swapping crypto perpetuals. Find out the latest on dYdX’s offerings and features on our official blog, and eligible traders can start trading on dYdX today.
Disclaimer
The content of this article (the “Article”) is provided for general informational purposes only. Reference to any specific strategy, technique, product, service, or entity does not constitute an endorsement or recommendation by dYdX Trading Inc., or any affiliate, agent, or representative thereof (“dYdX”). Use of strategies, techniques, products or services referenced in this Article may involve material risks, including the risk of financial losses arising from the volatility, operational loss, or nonconsensual liquidation of digital assets. The content of this Article does not constitute, and should not be considered, construed, or relied upon as, financial advice, legal advice, tax advice, investment advice, or advice of any other nature; and the content of this Article is not an offer, solicitation or call to action to make any investment, or purchase any crypto asset, of any kind. dYdX makes no representation, assurance or guarantee as to the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, suitability, or validity of any information in this Article or any third-party website that may be linked to it. You are solely responsible for conducting independent research, performing due diligence, and/or seeking advice from a professional advisor prior to taking any financial, tax, legal, or investment action.
You may only use the dYdX Services in compliance with the dYdX Terms of Use available here, including the geographic restrictions therein.
Any applicable sponsorship in connection with this Article will be disclosed, and any reference to a sponsor in this Article is for disclosure purposes, or informational in nature, and in any event is not a call to action to make an investment, acquire a service or product, or purchase crypto assets. This Article does not offer the purchase or sale of any financial instruments or related services.
By accessing this Article and taking any action in connection with the information contained in this Article, you agree that dYdX is not responsible, directly or indirectly, for any errors, omissions, or delays related to this Article, or any damage, injury, or loss incurred in connection with use of or reliance on the content of this Article, including any specific strategy, technique, product, service, or entity that may be referenced in the Article.







